- 1. What are the different phases of normal wound healing?
- 2. What are the main factors involved in delayed wound healing?
- 3. Which medicinal products affect wound healing?
- 4. What is the impact of topical corticosteroids on wound healing?
- 5. Is there a difference between wound healing in acute and chronic wounds?
- 6. How should you clean wounds?
- 7. What are the specific features of wound healing in children?
- 8. What are the specific features of wound healing in the elderly?
- 9. How to manage wound healing in cancer patients?
- 10. What are the specific features of wound healing in patients with burn injuries?
- 11. What dressing should be used according to the appearance of the wound?
- 12. What role do dermocosmetics play in wound healing?
- 13. Is there a role for alternative therapies in wound healing?
- 14. What advice should be given to patients to achieve an optimal scar (postoperative and post-trauma)?
- 15. What is a pathological scar and why does it develop?
- 16. How do you treat pathological scars?
- 17. How do you treat and heal a leg ulcer?
- 18. How do you treat and heal a pressure sore?
- 19. How do you treat and heal a foot wound in a diabetic patient?
- 20. What is the relationship between wound healing and mental health?
18. How do you treat and heal a pressure sore?
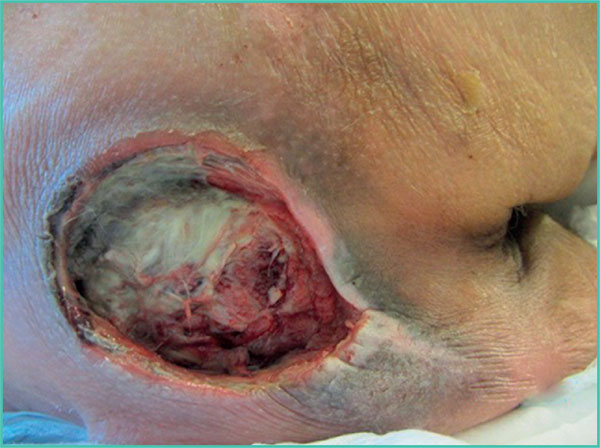
A pressure sore is a skin lesion of ischaemic origin caused by compression between soft tissue, a hard surface (e.g. floor or mattress) and a bony projection (Figure 13). By definition, such sores develop in areas of pressure such as on the heels, and on the lower part of the back and hips (e.g. sacrum and ischium). Many factors trigger pressure sores including malnutrition, poor vascular condition (especially in heel pressure sores with lower limb arteriopathy), and progressive cancer.
Healing pressure sores is dependent on the management of these triggering factors and offloading pressure from the wound. Healing can be slow in patients with multiple comorbidities, and more rapid in young subjects in an acute setting (e.g. prolonged immobilisation due to voluntary drug intake).
Pressure can be offloaded using a range of devices such as special mattress, mattress topper, pressure-relieving/offloading boots, etc.
 i
i
Figure 13. Pressure sore in the sacral region.
References
1. Singer AJ, Clark RA. Cutaneous wound healing. N Engl J Med 1999;341: 738-46.
2. Eming SA, Krieg T, Davidson JM. Inflammation in wound repair: molecular and cellular mechanisms. J Invest Dermatol2007; 127: 514-25.
3. Suivi en ville des plaies chroniques : ulcère veineux de jambe, escarre, plaie du pied diabétique. Assurance maladie, octobre 2015.
4. Plaies aiguës en structure d’urgence. Référentiel de bonnes pratiques. SFMU, 2017: 32 p.
5. Sgonc R, Gruber J. Age-related aspects of cutaneous wound hea- ling: a mini-review. Gerontology 2013; 59: 159-64.
6. Majtan J. Honey: an immunomodulator in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen 2014; 22: 187-92.
7. Opletalová K, BlaizotX, Mourgeon B, et al. Maggot therapyfor wound debridement: a randomized multicenter trial. Arch Dermatol 2012; 148: 432-8.
8. van den Broek LJ, Limandjaja GC, Niessen FB, Gibbs S. Human hypertrophic and keloid scar models: principles, limitations and future challenges from a tissueengineering perspective. ExpDer- matol 2014; 23: 382-6.
9. Prise en charge de l’ulcère de jambe à prédominance veineuse hors pansement. Recommandations HAS, 2006.
10. La compression médicale dans les affections veineuses chroniques. Fiche de bon usage HAS, 2010.
11. Edmonds M, Lázaro-Martínez JL, Alfayate-García JM, et al. Sucrose octasulfate dressing versus control dressing in patients with neu- roischaemic diabetic foot ulcers (Explorer): an international, multi- centre, double-blind, randomised, controlled trial [published correction appears in Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018; 6: 186-96.
12. Reinholz M, Poetschke J, Schwaiger H, Epple A, Ruzicka T, Gauglitz GG. The dermatology life quality index as a means to assess life quality in patients with different scar types. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2015; 29: 2112-9.

